This article is to make the procedure of setting up the WiFi. The Raspberry Pi is connected to Windows PC through Ethernet cable and the GUI is obtained using a VNC server. Although Raspberry Pi Model B comes with 100Mbps wired Ethernet, it is also essential to connect WiFi. The best arrangement is to purchase a cheap USB WiFi connector and utilize one of the USB ports to get to our WiFi home router. Setting up a Raspberry Pi utilizes the Raspbian OS to get to your remote system is simple – This article will guide you through the procedure.
Prerequisites & Equipment:
You will need the following:
-
A Raspberry Pi Model B or greater.
-
A USB WiFi Adapter (Edimax – Wireless 802.11b/g/n nano USB adapter is used here – it’s small and cheap!)
-
An SD Card flashed with the Raspbian OS (Here is a guide if you need)
-
Access to the Raspberry either via a keyboard and a monitor or remotely.
Before we continue I need to call attention to the significance of purchasing the compatible USB WiFi Adapter. Since not all the wifi dongles are plug and play to the Raspberry Pi. Some of the time you will need to download a driver to make them work. While drivers are typically accessible for Windows PCs – it is an alternate world for Linux and Raspberry Pi’s. This is the reason it is critical to purchase a WiFi Adapter that says “Linux” in the package. I utilize the Edimax – Wireless 802.11b/g/n nano USB adapter because I have found it to be cheap and very easy to work with. http://elinux.org/RPi_USB_Wi-Fi_Adapters — This link gives the list of plug and play compatible USB WiFi dongles for Raspberry Pi.
Adding WiFi adapter to the Raspberry Pi:
In this tutorial the Raspberrypi board is booted with the Ubuntu OS and is connected to the Ethernet port of a Windows7 PC. The board is connected to the internet connection as explained in the article Connecting the Raspberry pi to the internet. The IP address of the Raspberrypi board has been obtained to remote login in the TUI using the PUTTY and is remotely accessed using VNC.
After booting and logging-in you want to make sure that the new wireless adapter is found by Raspberry Pi. To look at which peripherals the operating system found when booting run the following command:
lsusb
This will give the list of USB devices connected to the Raspberry Pi.
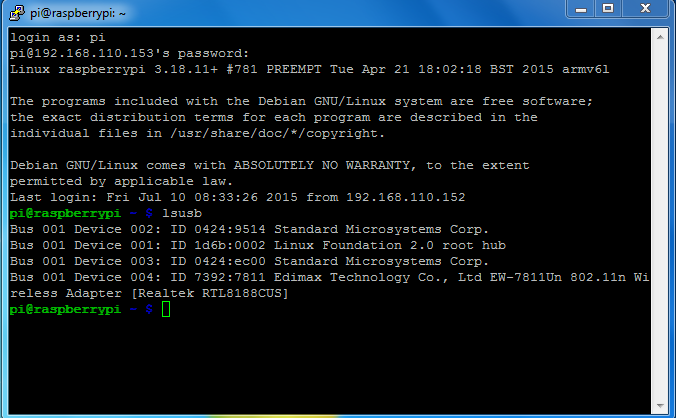
Fig. 2: Detecting USB Devices Connected To Raspberry Pi
Your device should be in the list. Followed by this command will ensure that WiFi dongle is Recognized.
dmesg | more
You can use the space-bar to scroll down a page at a time – towards the end you will see something similar to the following lines:

Fig. 3: Raspberry Pi Recognizing The USB Device
This means that the operating system recognized the USB WiFi Adapter using one of the built-in drivers (you can return to the terminal by pressing “q”). All that is left is to configure your WiFi connection.
Adding the network details to the Raspberry Pi:
Open a Terminal session enter the following command into it:
sudo nano /etc/network/interfaces
This will open the file in nano editor. After opening the file in nano, you will see a screen like this:
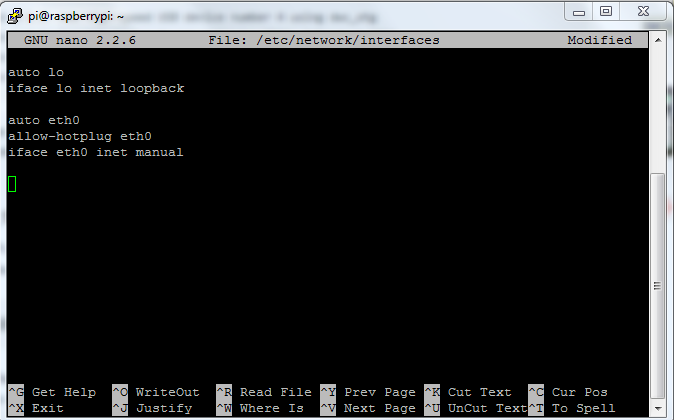
Fig. 4: Adding Network Details To Raspberry Pi
To configure your wireless network you want to modify the file such that it looks like the following:
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
auto eth0
allow-hotplug eth0
iface eth0 inet manual
auto wlan0
allow-hotplug wlan0
iface wlan0 inet manual
wpa-conf /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf
After editing the file you should see something like the following:
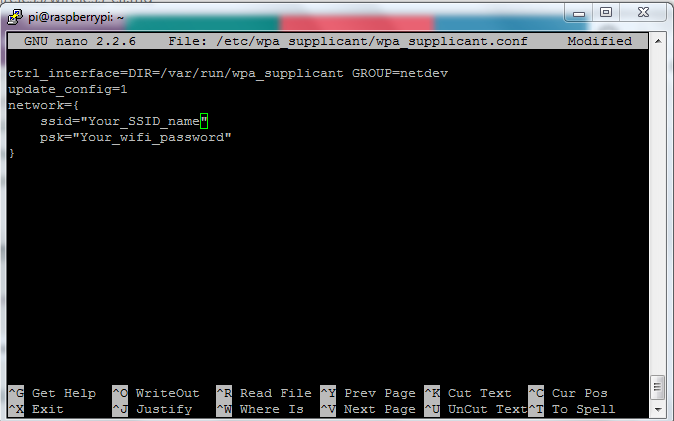
Fig. 5: Editing A File In Raspberry Pi To Configure Wireless Network
To save the file, press Ctrl+O this will write the file to the disk – afterwards you can exit nano by pressing Ctrl+X. If nano asks if you want to Save modified buffer? Press “Y” followed by hitting enter to confirm the filename.
Now open the wpa-supplicant configuration file in nano by entering this command:
sudo nano /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf
Go to the bottom of the file and add the following:
network={
ssid=”Your_SSID_name”
psk=”Your_wifi_password”
}
Now save the file by pressing ctrl+x then y, then finally press enter.
At this point, wpa-supplicant will normally notice a change has occurred within a few seconds, and it will try and connect to the network. If it does not, either manually restart the interface with sudo ifdown wlan0 and sudo ifup wlan0, or reboot your Raspberry Pi with sudo reboot.

Fig. 6: Testing Raspberry Pi Connected To Wifi
You can verify if it has successfully connected using ifconfig. If the inet addr field has an address beside it, the Pi has connected to the network. If not, check your SSID and password are correct.
You may also like:
Filed Under: More Editor's Picks, Raspberry pi, Tutorials






Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on EDAboard.com and Electro-Tech-Online.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.