This article is in continuation of PWM generation using AVR timer. In the previous article, PWM generation using Phase correct PWM mode is described. However, there are some applications like DAC, power regulation and rectification etc. which require high frequency PWM wave. The PWM generation using Fast PWM mode is suitable for such applications. This article focuses on Fast PWM mode of AVR Timer.
The Fast PWM mode is based on single-slope operation. In single slope operation, the register TCNTn counts from bottom value to maximum value and its value resets to zero. The counting starts again from bottom. The register OCRn compares the value with the TCNTn register constantly. If the timer is configured in non-inverting mode, PWM output pin (OCn) goes low when the value of the above two registers matches. The OCn pin becomes high when the TCNTn register reaches at bottom value. In inverting mode OCn pin behaves opposite to non-inverting mode. For timer 0 fast PWM mode, following table shows the functionality of COM 0[1:0] bits.

Fig. 2: COM 0 Bit Values and Description in AVR
Frequency of fast PWM mode signal is twice than Phase Correct PWM mode signal because of its single slope operation.
Output frequency of fast PWM signal = Crystal frequency÷(Prescaler ×256)
Objective: Compare output waveform of Phase correct PWM mode and Fast PWM generated signal.
For this objective Timer 0 is configured in Phase correct PWM and Timer 2 is configured in Fast PWM mode. The Duty cycle of signals is set to 50%.
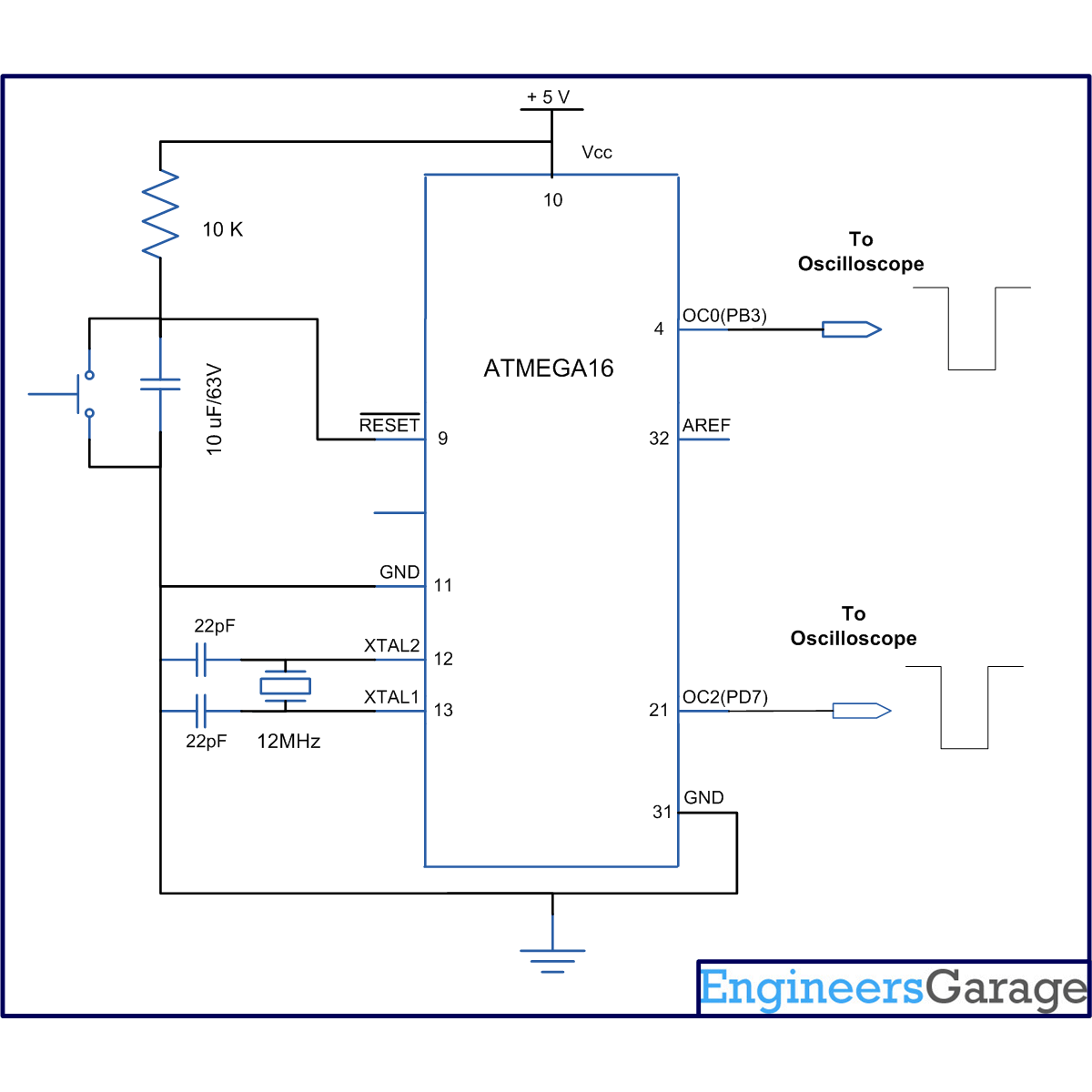
Circuit description:
The connection of ATmega16 is shown in circuit diagram. Since, Timer0 and Timer2 are used to generate PWM wave then output will be taken on OC0(PB3) and OC2(PD7) pins respectively.
Programming steps:
The programming steps to configure Phase correct PWM mode is similar as used in previous article. The following steps are written to configure the Timer2 for Fast PWM mode:
1. Select Fast PWM mode by programming WGM2 [1:0] bit.
2. Program COM2[1:0] and select inverting or non-inverting mode.
3. Set OC2 pin as output pin.
4. Set OCIE2 bit of TIMSK register.
5. Enable global interrupt by “sei()” command.
Output waves:
Phase correct PWM wave frequency by formula:
Output frequency= Crystal frequency÷(Prescaler ×510)
= 12000000 ÷ (8×510)
= 2941.17 Hz = 2.941KHz
Practically, the output wave form has frequency of 2.942 KHz with 50% duty cycle.
Fast PWM frequency by formula:
Output frequency= Crystal frequency ÷ (Prescaler ×256)
= 12000000 ÷ (8×256)
= 5859.375 Hz = 5.859 KHz
Practically, the output wave has frequency of 5.86 KHz with 50% duty cycle.
This experiment proves that Fast PWM wave has twice the frequency of Phase Correct PWM wave.

Fig. 3: Output Waveform Comparison of Fast PWM and Phase Correct PWM waves in AVR
Project Source Code
###
// Program to use fast PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) Mode of AVR microcontroller Timer#include<avr/io.h>#include<util/delay.h>#include<avr/interrupt.h>#define FREQ 12000000#define duty_cycle 50 // duty cycle require#define prescaler 8#define OCR_value ((duty_cycle*256)/100) //OCR value calculationvoid t0_pwm_init(void);void t2_fastpwm_init(void);int main(){t0_pwm_init();t2_fastpwm_init();sei();while(1);}void t0_pwm_init() // initialization for Phase Correct PWM signal using timer 0{// WGM0[1:0]= 01, for Phase Correct PWM mode// COM0[1:0]= 10, to select non inveting mode// CS0[2:0] =010. for prescaler=8TCCR0=(1<<WGM00)|(2<<COM00)|(2<<CS00);DDRB|=(1<<PB3); // selcet OC0 as output pinTIMSK|=(1<<OCIE0); //enable Output compare interrupt}void t2_fastpwm_init() // initialization for Phase Correct PWM signal using timer 2{// WGM2[1:0]= 11, for Fast PWM mode// COM2[1:0]= 10, to select non inveting mode// CS2[2:0] =010. for prescaler=8TCCR2=(1<<WGM20)|(1<<WGM21)|(2<<COM20)|(2<<CS20);DDRD|=(1<<PD7); // selcet OC2 as output pinTIMSK|=(1<<OCIE2); //enable Output compare interrupt}ISR(TIMER0_COMP_vect) // interrupt subroutine{OCR0=OCR_value; // put OCR value}ISR(TIMER2_COMP_vect) // interrupt subroutine{OCR2=OCR_value; // put OCR value}###
Circuit Diagrams
Project Components
Project Video
Filed Under: AVR.
Filed Under: AVR.


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.