
Fig. 1: Image showing DC motors attached on Line Follower Robot

Fig. 2: Image showing IR Sensor Modules attached on Line Follower Robot

Fig. 3: Image showing Castor Wheel attached on Line Follower Robot
REQUIREMENTS FOR LINE FOLLOWER ROBOT:
1. AT89S52 (8051 microcontroller by ATMEL Corp.)
2. L293D (16 pin IC)
3. 2 X DC geared motors
4. 2 X wheels
5. 2 X IR sensors (module)
7. 7V-8V Lithium Ion battery
8. Castor (3 wheel for support
9. Chassis
Line follower robot is a bot which can follow a particular line. Its a very good project to start with, for people who are interested in robotics and embedded systems.
In this case, it will follow a black line on a contrasting white background surface.
This bot comprises of a sensor section, driver section and a microcontroller to process the sensor values and correspondingly operate the motor driver section.
Sensor section consists of IR sensors (2 in this case)
Driver section involves the working of geared DC motors (via L293D IC)
There are basically two orientations for the IR sensors to work.
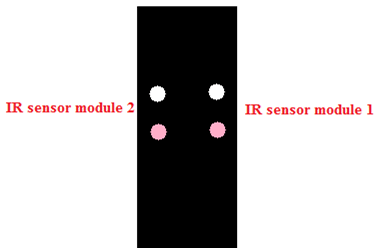
Fig. 4: Image showing orientation of IR sensors on the IR module
In the above case the sensors lie inside the black line

Fig. 5:
In this case the sensors lie outside the black line
In both the cases these sensors will help the bot to follow the line. The difference will be in their coding part.
Working
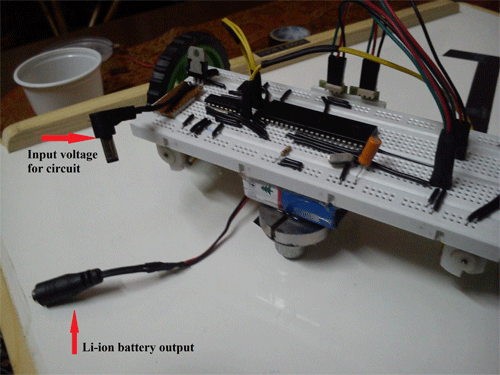
Fig. 6: Prototype of 8051 Microcontroller based Line Follower Robot
To study the working of IR sensors visit my previous article: automatic room lighting
Sensors provide high value (1) when on white surface and low value (0) when on black surface.
Now talking about L293D, this IC will provide the desired voltage for the motors to operate properly. For its working visit: Interfacing L293D with 8051
When we work with case 1, the bot will move forward only when both sensors return 0(they are on black surface), it will move left when IR1 returns 1(on white surface) and IR2 returns 0(on black surface), it will move right when IR1 returns 0(on black surface) and IR2 returns 1(on white surface) and finally when both the sensors return 1(on white surface) the bot will stop.
When we work with case 2, the bot will move forward only when both sensors return 1(they are on white surface), it will move left when IR1 returns 1(on white surface) and IR2 returns 0(on black surface), it will move right when IR1 returns 0(on black surface) and IR2 returns 1(on white surface) and finally when both the sensors return 0(on black surface) the bot will stop.
When it comes to battery, one should always opt for those batteries which are high in performance and cheap. I’ll suggest to use Li-ion(cell phone batteries) because they are cheap and rechargeable.
You can connect two Li-ion batteries in series to get a voltage of 8V sufficient enough for driving 2 DC geared motors properly for long time.
Warning: Be careful while recharging the batteries as they may explode when not charged properly.
I’ll suggest you to use a 9V adapter to charge these kinds of batteries (when 2 batteries connected in series) for not more than 2 hours.
Project Source Code
### #include<reg51.h> sbit SR=P1^7; ////right sensor sbit SL=P1^6; ////left sensor sbit MRp=P1^4; ////right motor +ive terminal sbit MRn=P1^3; ////right motor -ive terminal sbit MLp=P1^2; ////left motor +ive terminal sbit MLn=P1^1; ////left motor -ive terminal void main() { SR=SL=1; MRp=MLp=MRn=MLn=0; while(1) { if(SR==0 && SL==0) { MRp=1; MRn=0; ////moving forward MLp=1; MLn=0; } if(SR==1 && SL==0) { MRp=1; MRn=0; ////moving left MLp=0; MLn=1; } if(SR==0 && SL==1) { MRp=0; MRn=1; ////moving right MLp=1; MLn=0; } if(SR==1 && SL==1) { MRp=0; MRn=0; ////stop MLp=0; MLn=0; } } } CODING: (case 2) #include<reg51.h> sbit SR=P1^7; ////right sensor sbit SL=P1^6; ////left sensor sbit MRp=P1^4; ////right motor +ive terminal sbit MRn=P1^3; ////right motor -ive terminal sbit MLp=P1^2; ////left motor +ive terminal sbit MLn=P1^1; ////left motor -ive terminal void main() { SR=SL=1; MRp=MLp=MRn=MLn=0; while(1) { if(SR==1 && SL==1) { MRp=1; MRn=0; ////moving forward MLp=1; MLn=0; } if(SR==1 && SL==0) { MRp=1; MRn=0; ////moving left MLp=0; MLn=1; } if(SR==0 && SL==1) { MRp=0; MRn=1; ////moving right MLp=1; MLn=0; } if(SR==0 && SL==0) { MRp=0; MRn=0; ////stop MLp=0; MLn=0; } } } ###
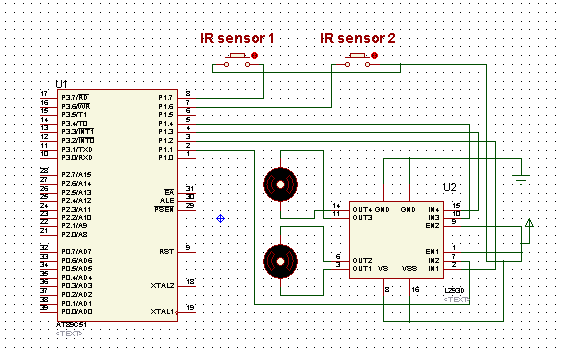
Circuit Diagrams
Project Video
Filed Under: Electronic Projects
Filed Under: Electronic Projects


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on EDAboard.com and Electro-Tech-Online.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.