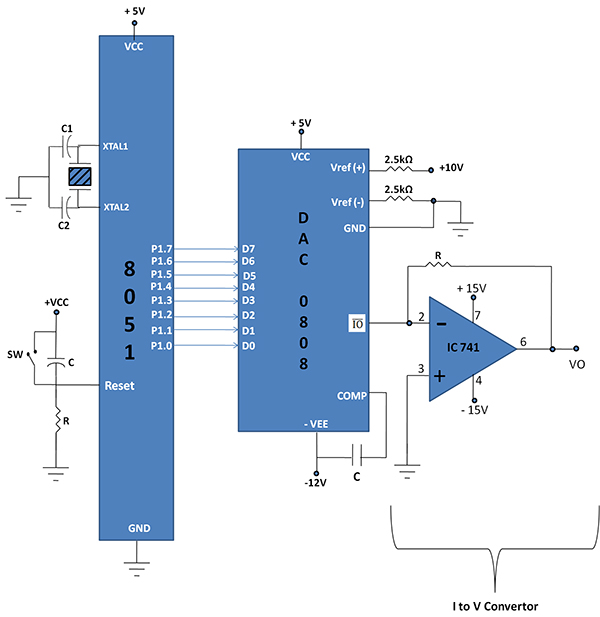
Fig. 1: Overview of DAC 0808 and 8051 Microcontroller Interfacing
We will see alternate DAC0832 IC interface to 8051. Let’s study briefly about DAC0832 IC. Fig 2 shows pin diagram of DAC0832 IC. It is 20 PIN DIP(Dual –in-Line Package) IC
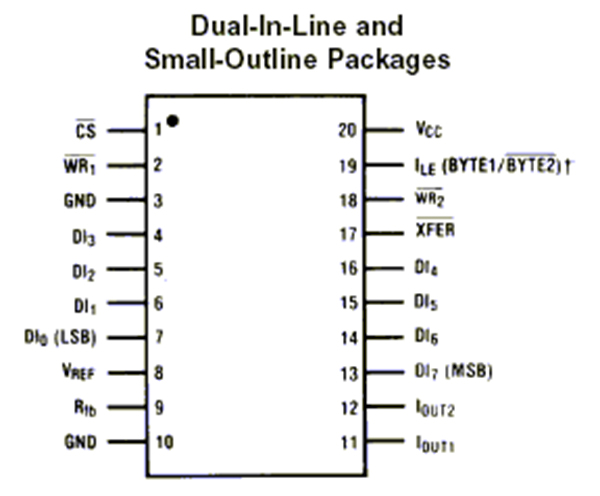
Fig. 2: Pin Diagram of DAC0832 Digital to Analog Converter IC
DAC0830 is an advanced CMOS/Si-Cr 8-bit multiplying DAC designed to interface directly with the 8080, 8048, 8085, Z80, and other popular microprocessors. A deposited silicon-chromium R-2R resistor ladder network divides the reference current. The circuit uses CMOS current switches and control logic to achieve low power consumption and low output leakage current errors. Special circuitry provides TTL logic input voltage level compatibility.
Technical specification of this IC:
Interfacing of 0832IC with 89s52 microcontroller is shown in Fig3. You can replace this microcontroller with P89v51RD2 IC. I have explained P89v51RD2 microcontroller in another article. This microcontroller is easily programmable via serial port(COM port) using FlashMagic utility (This utility can be downloaded from link www.flashmagictool.com/)
Microcontroller and Programming
You can program this microcontroller using EPROM or Universal programmer.
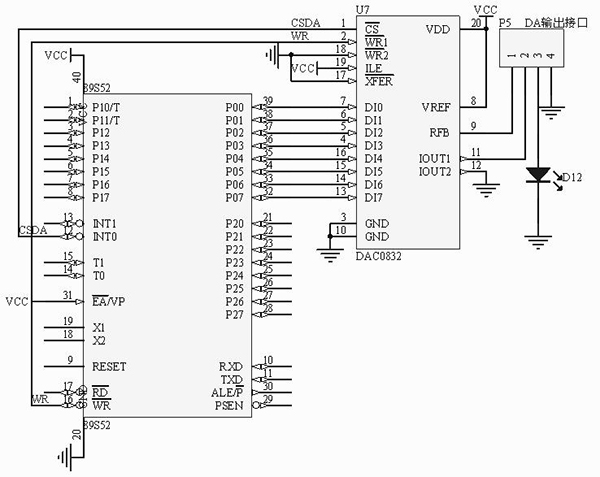
Fig. 3: DAC0832 IC Interfacing wiith 8051 Microcontroller Circuit Diagram
This microcontroller you can program using EPROM programmer or Universal programmer.
In embedded market independent DAC0832 modules are available for sale. I picked up one module which we use for our client. Fig 4 shows front side of DAC module and Fig 5 shows back side of DAC0832 module.

Fig. 4: Typical Image of DAC0832 Module
You type following program in evaluation keil version cross compiler. Create HEX file for this experiment and download that HEX file in the 8051 board. We are using Port P1 of 8051 to interface DAC module. Connect P1.0 to P1.0 of DAC module so on, you connect al 8 pins of Port1 to DAC module. Digital data is coming from 8051 microcontroller. DAC0832 will convert this data in to analog. We are using P3.3, P3.4, P3.5 pins for hand shaking of 8051 and DAC0832 IC. Connect P3.3 of microcontroller to active low CS signal of DAC0832 module and P3.4, P3.5 for WR1 and XFER respectively.
1)To generate sine wave through DAC 0832: Type this program.
The program is provided in above Sourcecode Section.
Above program is very easy to understand. Select IC by making CS=0 in program and then use super loop to show sine wave continuously at VOUT and GND signal of DAC0832 board.
Make WR1,XFER signal 1 in program to tell DAC about the start of conversion. WAVEVALUE[i]; statement transfers digital value form array to P1 of 8051. These are 12 values which can be increased for better result. Make WR1, XFER signal to “0” and create delay using _nop_(); statement multiple times.
Once conversion takes place, send analog output via LM358 to amplify analog signal. LM358 details are explained in other articles of engineersgarage website (http://www.engineersgarage.com/contribution/anjali/performing-experiments-with-lm358) .
You can check sine wave output from DAC0832 module on CRO by connecting Channel probe of CRO at Vout and GND of DAC module. Fig 5 shows sine wave output. As we provide 12 digital values, we don’t get super fine Sine wave, but by increasing values of Array, we can get better sine wave.

Fig. 5: Image showing Analog Sine Wave Output from 8051 Microcontroller observed on Oscilloscope
2) To generate triangular wave from DAC0832: Type following program in Keil version 3 cross compiler.
|
/************************************************************************************* This program generates a triangular wave of 2kHz when Port1 is interfaced with DAC **************************************************************************************/ The Program is provided in the above Sourcecode section. |
Above program is very simple to understand. We are sending P1 += 0x05;
Value to port P1 of 8051 and these values are controlling DAC0832. We are sending incremental values using following loop.
do
{
WR1=1;
XFER=1;
P1 += 0x05;
WR1=0;
XFER=0;
}
while(P1<0xFF);
Microcontroller keep sending data from 0x05 to 0xFE and when this data become 0xFF, it comes out from loop and we are getting RAMP output due to this loop. In second loop we are decrementing value using
P1 -= 0x05;
Statement and again test for P1< 0xFF. After incrementing the value of P1 in first loop and decrementing it in the second loop, we get triangular waveform as shown in Fig 6.

Fig. 6: Image showing Analog Triangular Wave Output from 8051 Microcontroller observed on Oscilloscope
3)To generate square wave using DAC0832 module :Tyep ethis program in keil version 2 and generate HEX file and download indidually to get square wave.
|
/********************************************************************************* This program generates a square wave of 2kHz when Port1 is interfaced with DAC ***********************************************************************************/ The program is provided in the above Sourcecode Section. |
Send 0xFF and 0x00 value from the Port 1 of 8051 and this enters into DAC0832 IC which processes digital data and gives out Analog output. In this code, we write separate void delay(int time) function. This function is having one argument ‘time”, whenever we call this function in main program, we have to pass some integer number. In above code, we write delay(1);, this pass “1” and value of time becomes 1 inside delay() function.
Use simple for loop to create delay, you have to understand that upper for loop is not having semicolon and inner for loop is having semicolon. *(didn’t get the term “for loop”) There is typical meaning to that. When we want to execute inner loop completely then we write a code like this. Here initial value of “i” will be “0” and internal loop will be executed three times where j=0, j=1 and j=2 then conditions in for loop will be false and processor will come out from inner loop. Then again “i” will be incremented to “1”. This happens due to i++ statement.
for(i=0;i<=time;i++)
for(j=0;j<=2;j++);
Fig 7 shows output of square wave using DAC0832 module.
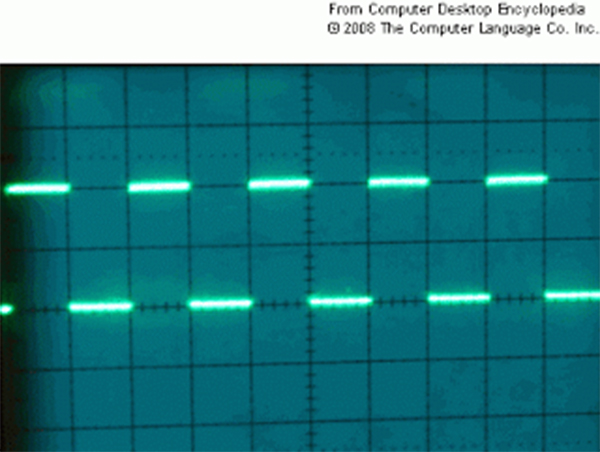
Fig. 7: Image showing Analog Square Wave Output from 8051 Microcontroller observed on Oscilloscope
Project Source Code
###
To generate sine wave through DAC 0832: Type this program
#include<reg51.h>
#include<intrins.h>
sbit CS=P3^3;
sbit WR1=P3^4;
sbit XFER=P3^5;
void main() // Start of main() function
{
int WAVEVALUE[12] = { 128,192,238,255,238,192,128,64,17,0,17,64};
// Create a look-up table (array) named WAVEVALUE to send appropriate
//values to DAC so that a sine-wave is generated. Refer to table
int i;
// variable i used in for loop
CS=0;
while(1)
// Infinite loop, the program will run forever
{
for(i=0;i<12;i++)
{
WR1=1;
XFER=1;
P1 = WAVEVALUE[i];
// All the values in the array is sent to DAC one by one
WR1=0;
XFER=0;
_nop_();
_nop_();
_nop_();
_nop_();
_nop_();
_nop_();
}
// Value 83 is sent to delay with creates a total delay of 996 msec.
//which roughly translates into sine-wave of 1Khz
}
}
/*************************************************************************************
This program generates a triangular wave of 2kHz when Port1 in interfaced with DAC
**************************************************************************************/
#include<reg51.h>
sbit CS=P3^3; //CS of DAC 0832
sbit WR1=P3^4;//WR1 of DAC 0832
sbit XFER=P3^5;
void main() // Start of main() function
{
P1 = 0x00; // Initialize Port 1 as Output Port
CS=0;
while(1) // Infinite Loop
{
do
{
WR1=1;
XFER=1;
P1 += 0x05;
WR1=0;
XFER=0;
}
while(P1<0xFF);
do
{
WR1=1;
XFER=1;
P1 -= 0x05;
WR1=0;
XFER=0;
}
while(P1>0x00);
}
}
/*********************************************************************************
This program generates a square wave of 2kHz when Port1 in interfaced with DAC
***********************************************************************************/
#include<reg51.h>
sbit CS=P3^3;
sbit WR1=P3^4;
sbit XFER=P3^5;
void delay(int time); // delay() function prototype, this function generates delay = (time x 1msec)
// For example delay(500). Generates delay of (500 x 1msec) = 500msec
void main() // Start of main() function
{
P1 = 0x00; // Initialize Port 1 as Output Port
while(1) // Infinite Loop
{
WR1=1;
XFER=1;
P1 = 0xFF; // Send maximum value to Port1 for
//getting High Period of Square Wave
WR1=0;
XFER=0;
delay(1); // Call delay() to get 1msec of duty cycle
//for High Period
WR1=1;
XFER=1;
// Delay calculated as 1 x 1msec = 1msec
P1 = 0x00;
// Send minimum value to Port1 for getting
//Low Period of Square Wave
WR1=0;
XFER=0;
delay(1);
// Call delay() to get 1msec of duty cycle for Low Period
}
}
void delay(int time) // Start of delay() function.
//Delay() function generates delay of desired amount.
{
int i,j; // Initialize variable i,j for generating Delay
for(i=0;i<=time;i++)
// Use Nested For loops to generate desired
// amount of delay.(Repeat 1ms delay by value
// stored in variable 'time')
for(j=0;j<=2;j++); // this for loop generates delay of
//1 millisecond
}
###
Filed Under: Electronic Projects


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.