Data science is set to prevail in the 21st century. By the late 1900s, computers had already become an inseparable part of human civilization, all thanks to Bill Gates and Steve Jobs. This followed the glorious rise of the internet all across the globe. Then with mobile phones, smartphones, and wearables, almost every person on earth is equipped with a handheld computer. And just next, billions of mobile devices are joined by billions of IoT devices.
This century is all about computers and data. From the invention of the first computer, there have been efforts to make these machines better and more intelligent. The computers themselves are marvelous machines, and the internet made them more intelligent and valuable. While the internet was spanning across the globe connecting all sorts of computer devices irrespective of geography, there has been a gradual development towards making computers inherently more intelligent using Artificial Intelligence.
I have my definition of computers. I define computers as ‘ digital electronic circuits that have a set of instructions that, when coded to execute in specific sequences, can perform specific computing tasks. The computer programs have been natively sequences of instructions on input data, which has somehow limited the capabilities of computers to be autonomous and brilliant machines. The computers always need a program for doing anything useful. A human writes a program, so there is always a need for human intervention from developing to maintaining computer programs.
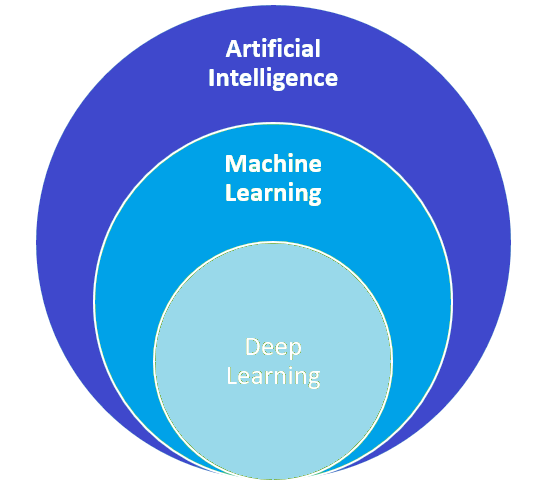
Artificial Intelligence is an effort to make computers intelligent. AI aims to make computers self-aware and self-reliant by infusing the capability to think themselves. Artificial Intelligence is a multi-disciplinary field that includes machine learning, deep learning, data mining, computer vision, natural language processing, and several other disciplines. Firstly, AI involves making computers self-aware utilizing computer vision, natural language understanding, and imitating other senses. Secondly, AI involves imitating the cognitive functions of human beings like learning, reasoning, and problem-solving. From the perspective of computer theory, AI aims to equip computers to decide the program themselves instead of following a user-defined program. Here, the self-designed program can do anything that humans do by their unique ability of intelligence and discernment. A formal definition of artificial intelligence is as follow –
“Artificial Intelligence is the area of computer science that deals with giving machines ability to seem like they have human intelligence.”
Intelligence is a broad term that is yet not fully understood by humanity. The multifaceted and multi-dimensional nature of the human brain is an unsolved puzzle. Replicating human intelligence is still a faraway dream. Artificial Intelligence, at its current juncture, is all about neural networks. Currently, AI uses the same CMOS hardware that typical computers are built from. The current AI is focused on developing algorithmic functions that infuse human-like intelligence. The discipline focuses on replicating human intelligence through Artificial Neural Networks (ANN), like software copies of human neurons. AI is a multi-disciplinary field involving computer theory, mathematics, statistics, probability, data-mining, and domain-specific expertise.
Machine Learning is a subset of Artificial Intelligence. Learning is one of the essential aspects of the human brain, along with memorizing and analyzing. Machine Learning aims at building computer models (software models) that let the computer determine a program (how it has to process data) on its own based on its experience of the past data stream or given historical data (inputs). The computer does not follow a user-defined program; instead, it determines its program based on its experience of past inputs and outcomes. This is similar to how humans themselves learn. Based on their experience (through senses like sight, hearing, touch, taste, or smell), humans observe cause-effect relationships and determine their actions, reflexes, and responses accordingly. A machine learning model must return a program that has expected outcomes. The closer its program is to give expected outcomes, the higher is its performance.
There are two definitions of machine learning that are widely accepted. One is given by Arthur Samuel as follows.
“Machine learning is the field of study that gives computers the ability to learn without being explicitly programmed.”
This is an informal definition. Tom Mitchell offers a modern definition, which better demonstrates the concept and working of machine learning. It is as follows.
“A computer program is said to learn from experience E with respect to some class of tasks T and performance measure P, if its performance at tasks in T, as measured by P, improves with experience E”
Deep Learning is a sub-field of machine learning. Suppose machine learning is an effort to replicate the aspect of ‘learning from observing data patterns’ and ’cause-effect relationships,’ i.e., by correlating inputs and outcomes. In that case, deep learning is an effort to replicate the aspect of ‘learning about the objects themselves,’ i.e., building representational data or practical concepts from input data. If machine learning focuses on understanding actions & outcomes related to objects, deep learning is focused on understanding the objects themselves.
Humans are not perfect at anything the first time. They learn things through multiple efforts and practice. After a lot of practice, they become proficient in something. Every new effort adds to their performance and proficiency, creating a better understanding of cause-effect relationships and improved understanding of the objects. For example, you are learning to throw a ball. You know to do a perfect throw by multiple attempts, gradually building relevant motor skills required to do a perfect throw. This involves the development of relevant motor skills and understanding the ball itself — the knowledge of its weight, the effect of air on its flight, etc.
Similarly, a machine learning model may not return a program with exactly the expected outcome. But, the results can improve over time with a better understanding of the input data. Machine learning is about utilizing past input and outcomes for improving future outcomes. Deep learning is about building concepts using input data using useful representations of input data.
Currently, deep learning is just a popular alias for neural networks. Deep learning is focused on representing data as a layered hierarchy of concepts. While traditional machine learning is limited to correlating inputs (data) and outcomes or determining data patterns within input data, deep learning emphasizes finding representations (concepts and possible outcomes) in the input data itself. Deep learning is particularly useful in feature extraction and engineering. Deep learning is defined as follows.
“Deep learning is a type of machine learning based on artificial neural networks in which multiple layers of processing are used to extract progressively higher-level features from data.”
Natural Language Processing is a related multi-disciplinary field. It aims to enable machines (computers) to understand, process, and interact with natural human languages. Language and mathematics are the two major accomplishments of humanity that made it superior to other living species. Language enabled humans to communicate, pass and store subjective knowledge, while mathematics allows humans to communicate and store quantitative knowledge. Natural Language Processing and Text Analytics involve parsing natural human language, identifying knowledge and semantic representations, natural language processing, and natural language generation. NLP is defined as follows.
“Natural language processing is the application of computational techniques to the analysis and synthesis of natural language and speech.”
Some practical applications of NLP are text-to-speech, speech recognition, speech-to-text, machine translation, information extraction, text categorization, text summarization, topic segmentation, sentiment analysis, and emotion analysis.
Computer Vision is another related discipline. Computer vision aims to replicate human vision, and it involves image processing for scene recognition, object recognition, object classification, feature extraction, gesture recognition, and gesture detection. Computer vision takes many concepts and algorithms from artificial intelligence and machine learning. Computer vision is defined as follows.
“Computer vision is the field of artificial intelligence that enables computers and machines to identify objects and derive other meaningful insights from digital images, videos, and other visual inputs.”
Applications of Artificial Intelligence
Although Artificial Intelligence is in its infancy, it is still widely used across several verticals. According to an estimate in 2020, 37% of organizations are already using artificial intelligence in one or the other form. Most of the artificial intelligence applications are specific technologies like computer vision, natural language processing, speech recognition, machine learning, and expert systems. Let us look at some of the vertical-specific applications of AI:
Healthcare: AI has found many different applications in the healthcare sector. The healthcare industry uses artificial intelligence to detect diseases using medical history, analyze chronic conditions, cancer treatment, and discover new drugs using historical medical data, lab reports, and intelligence.
E-commerce: E-commerce companies are using artificial intelligence to personalize shopping with the help of recommendation engines that use browsing data and customer preferences as inputs. Using natural language processing, e-commerce sites build chatbots and virtual shopping assistants providing real-time customer care and assistance. The companies also use AI to identify fake reviews and credit card frauds.
Social Media: Like e-commerce, social media sites also use AI to better engage with their community. For example, Meta Platforms Inc. (Facebook) uses an NLP tool Deeptext to analyze conversations and perform automatic language translations. Twitter uses AI to forward tweets of particular interests, identify objectionable content, and detect fraud. Similarly, most social media sites use artificial intelligence to personalize content, manage ads, perform translations, identify fraudulent and objectionable activities.
Marketing: The marketing sector uses artificial intelligence to derive valuable insights from business reports and produce automated analytics. Apart from analytics and business decision making, corporate are also using AI for customer relationship management (CRM), customer services, and management of post-sale services.
Education: The use of AI in education is currently limited to online education providers. The education websites use AI to recommend courses, track student progress, personalize lessons, and manage feedback and user interactions.
Automation and Robotics: Robotics is one of the fields concurrently adopting artificial intelligence. With the help of computer vision, voice control, and expert systems, robots are now made to work with human workers with multi-tasking capabilities. Computer vision, sensor networks, and artificial intelligence are widely used in CNC machines and assembly lines to reduce errors, perform automatic corrections and improve productivity.
Transportation: App-based cab services and vehicle sharing services widely use AI to track real-time traffic, optimize routes and minimize operational costs. AI is also being used to improve the transportation industry’s inventory management and operations management.
Agriculture: AI finds applications in agriculture, particularly in polyhouse, hydroponic, and aquaponic. In these types of specialized farming, AI is being used to track the growth of the produce, identify weeds, pest control, optimize climate conditions, control operations management, manage harvesting, and maximize production. With the help of automation and artificial intelligence, large farms can be managed with a limited number of workers. In traditional farming also, AI is being used to predict weather conditions, take early decisions accordingly, manage irrigation, and for smart harvesting of crops using AI bots. In the future, AI and IoT can be used for automated remote management of farms and crops.
Trading: Algorithmic trading is the new trend in stocks and investment. AI bots are used for stock trading, cryptocurrency trading, commodity trading, and forex trading.
Gaming industry: The gaming industry uses AI to track user behavior, automatically personalize game settings, create smart non-player characters, and personalize difficulty levels.
Self-driving cars: One major initiative involving artificial intelligence is self-driving cars. These vehicles will use machine learning, computer vision, navigation services, and artificial intelligence to self-drive without human intervention. The AI is also used for intelligent navigation, enhancing in-vehicle experience, and controlling traffic management.
Security and Surveillance: The new security and surveillance systems will primarily rely on biometrics, computer vision, voice analysis, and big data. These systems will be capable of automatic detection of suspects, early detection of unlawful activities, tracking smuggling and money laundering, and tracking suspects for intelligence inputs.
Future of AI
The current artificial intelligence is mainly software-based, and it uses the same CMOS circuits that typical computers are built on. In the future, artificial intelligence will be based on specialized circuits and architectures with human-brain-like designs. The machines will be more sensible with vision, hearing, touch, taste, smell, and even the sense of emotions and intuition. The current applications of AI are confined to solving specific tasks particular to a given vertical. The current AI primarily involves identifying data patterns, making predictions, and testing outcomes in machine learning or deep learning. Artificial intelligence is applicable at the cloud-end, where it has big data at its disposal. The future AI will be mainly onto the edge devices with specialized hardware architectures. We can hope that AI may become an authentic replica of human intelligence and exhibit the same multifaceted, multi-dimensional, and genuinely autonomous intelligence as humans, which is its ultimate goal.
Conclusion
The 21st century belongs to computers. These computers are existent in the form of mainframes, servers, desktops, mobile computers, and embedded computers. Computer technology is going through two internet and artificial intelligence revolutions simultaneously – the internet connects all sorts of computer devices across the globe, enabling them to share valuable data. Artificial intelligence is making them inherently intelligent that they could derive valuable insights from the data on their own without human intervention. Artificial Intelligence has the potential to rewrite the age-old computer theory by making the computers self-aware and autonomous in contrast to their current avatar of dependant machines running user-defined programs. Machine Learning is a subset of Artificial Intelligence that involves learning from experience, and Deep Learning is a field of machine learning focused on building concepts upon the data itself.
You may also like:
Filed Under: AI, Applications, Featured, Machine Learning, What Is








Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on EDAboard.com and Electro-Tech-Online.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.