Filters are used in various fields including telecommunications where bandpass filters are used in speech recognition and modems in the audio frequency range (0 Hz to 20KHz). In the central telephone offices, high-frequency (hundreds of MHz)bandpass filters are used for channel selection.
In data acquisition systems, low-pass noise filters and anti-aliasing low-pass filters are required for signal conditioning. Bandpass filters are used in power supply systems to suppress the noise of 50 Hz.
All pass filters are used to add time delay in each frequency component of a complex signal. As pass filters don’t filter any frequency components from complex signals, they just add a linear phase shift in each frequency component of a signal.
At higher frequencies (greater than MHz), these filters consist of passive components like inductors, capacitors, and resistors and are called RLC filters. But at lower frequencies (below 1MHz), the inductor values increase and size, which makes the design bulky.
In these cases, an active filter comes into play. Active filters are filter circuits that consist of an operational amplifier with a combination of passive components and provide LRC-like filtering at lower frequencies.
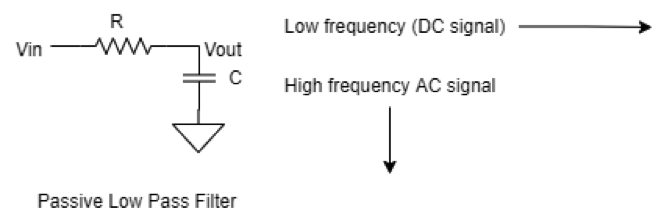
RC low-pass filter
As shown below, a low-pass filter can be created by placing a resistor in series with the input signal and a capacitor in parallel with the input signal.
The cutoff frequency of the low-pass filter is given by
Fc = 1/2piRC
Fc – Cutoff frequency
Pi – 3.141
For example:
R – 1K ; C – 10nF
I was doing math and calculating the cutoff frequency of the above values.
Fc = 1/2*3.141*1K*10nF = 15.9 KHz
That means frequencies greater than 15.9 kHz will be attenuated, and frequencies below 15.9 kHz will be in the pass band.
LR low pass filter
LR low pass filter is composed of an inductor in series with the input signal and a resistor in parallel with the input signal and works the same as the RC low-pass filter; it attenuates the high-frequency band from a signal and attenuates more and more as the frequency increases.
The LR filter circuit works on the principle of inductive reactance. That means how the resistance or impedance of the inductor behaves with frequency passing through it. Resistance has fixed resistance. But the inductor has different resistance for different frequency signals as capacitors do.
The inductor produces high impedance or resistance for high-frequency signals and very low resistance for low-frequency signals. It behaves just the opposite of a capacitor. Because of this, the resistor placement place is different in the RL circuit. The above circuit effectively blocks the high-frequency signal and passes the low-frequency signals.
The cutoff frequency is given by
Fc = R/2PiL
If L =210mH & R = 10K in the above circuit,
then Fc will be 7.58KHz
That means if a complex signal is passed through the above filter, it will attenuate frequencies above 7.58KHz and let the below frequencies pass.
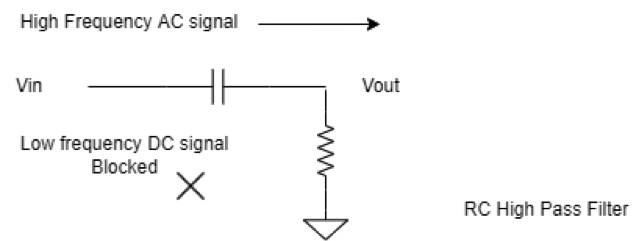
RC high-pass filter
A simple passive RC high-pass filter can be designed by using a capacitor in series with the input signal and a resistor in parallel with the input signal, as in the below circuit.
The capacitor is a reactive device that offers different resistance to signals with different frequencies interesting through the capacitor. A capacitor is a reactive device that offers very high resistance to a signal with a very low frequency or DC signal and low resistance to a very high-frequency signal. As a capacitor offers high resistance or impedance to a DC or low-frequency signal, it blocks them from entering through a capacitor.
The cutoff frequency of the RC high-pass filter is given by the formula given below.
Fc = 1/2PiRC
A high-pass filter is commonly used in various device circuits, like the microphone. As the microphone works on both AC and DC, it records the AC signals entering it and operates on the DC supply. Therefore, it becomes necessary to use it in the microphone recording circuit.
If, in the above RC high-pass filter C = 10nF and R = 1K
Then Fc = 1/2*3.14*1K*10nF
Fc = 15.923 KHz
The cutoff frequency is calculated at 15.923 kHz, meaning if a complex signal is passed through the above circuit, signals with a frequency below 15.923 kHz will be blocked, and frequency components above that will pass.
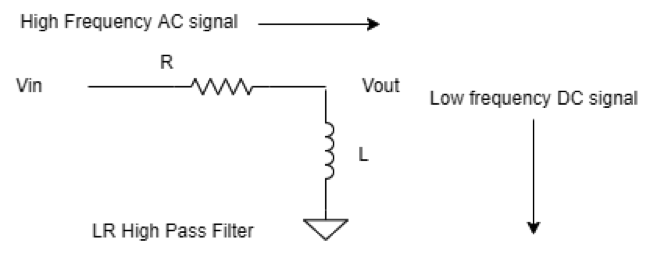
LR high pass filter
An LR high-pass filter can be composed of placing a resistor in series with an input source signal and an inductor in parallel with the input source signal entering in the circuit.
An inductor has inductive reactance that varies with different signals of frequencies and offers great resistance to high-frequency signals and very low resistance to low-frequency signals. It provides high resistance to high-frequency signals, so high-frequency current does not pass the inductor, and the signal chooses a low resistance path and travels to output. But low-frequency current faces very low resistance offered by the inductor, so it passes through the inductor to the ground.
The formula gives the cutoff frequency.
Fc = R/2PiL
For example, in the above circuit
R = 10K; L = 470mH
Then the calculated cutoff frequency is
Fc = 3.39KHz
If a signal is passed through the above circuit, then frequency components of that signal below this frequency will be attenuated, and higher than this will be seen on the output.
You may also like:
Filed Under: Featured Contributions, Hardware Filters, Tutorials





Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.