An ac-dc converter is commonly used in many devices. Also called a rectifier, it converts alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). Most electronic devices, such as computers, smartphones, and electronic circuits, operate on DC power. However, there are different ways to convert AC into DC power (as discussed in the previous AC-to-DC conversion article). For…
Nexperia enables high-power load switching in space-constrained applications
Nexperia, a semiconductor provider, has released a new series of 500 mA dual resistor-equipped transistors (RET) in ultra-compact DFN2020(D)-6 packaging. These devices have been designed for load switching in wearables and smartphones. They’re also ideal for use in digital circuits with higher power requirements, such as space-constrained computing, communications, industrial, and automotive applications. Notably, the…
Nexperia and KYOCERA AVX to produce silicon-carbide rectifier module
Nexperia, a semiconductor provider, announced it has entered into a partnership with KYOCERA AVX Components, an international supplier of advanced electronic components, to jointly produce a new 650 V, 20 A silicon-carbide (SiC) rectifier module. The new rectifier module will be for high-frequency power applications ranging from 3 to 11 kW power stack designs —…
1.25V – 25V Variable power supply using bridge rectifier
The electronic devices are very sensitive to the fluctuations in the power fed to them. This problem can be solved by using regulated power supply for them. This [[wysiwyg_imageupload::]]project about power supply circuit is equipped with an adjustable voltage regulator to adjust the output in accordance with the requirement. Adjustable voltage regulators have both line and load regulation which is better than standard fixed regulators. The circuit is made using following active and passive electronic components: 1. Bridge Rectifier2. Resistors3. Capacitors 4. Variable Resistors.5. Linear Voltage Regulator IC
Microchip’s advanced power modules qualified to aerospace standards
In the race to reduce aircraft emissions, developers increasingly are moving toward more efficient designs including electrical systems that replace today’s pneumatics and hydraulics powering everything from on-board alternators to actuators and Auxiliary Power Units (APUs). To enable next-generation aircraft electrical systems, new power conversion technology is required. Microchip Technology has announced its development with…
Insight – How Diode Works
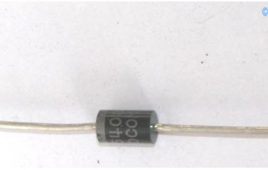
This component needs no introduction. One of the first semiconductor based engineering components, diodes are an indispensible necessity for any current modern gadget or circuit. They are the basic logic block – the most fundamental unit.These two terminal-ed nonlinear passive elements ideally conduct only one way and hence protect the circuit as well as the source from any damage. Diodes are widely used in rectifier circuits, limiters, communication circuits, multiplier circuits and signal clippers as well as clamper circuits. This Insight will give an in depth view of a diode’s physicality. Read more to find out about how a diode works through images of its internal and external parts such as epoxy layer, rubber coat, metallic shell, inner semiconductor traces etc.
Electronic Ballast
People have grown up with the sights and sounds of fluorescent lamps buzzing to life after a few attempts. As the new wave of energy saving appliances gripped the world, technology made the fluorescent lamps shrink in thickness as well as reduced the number of attempts made by lamps to shine their brightest. Today many homes use energy Saver CFL lamps and fluorescent tubes which start giving light the moment they are switched on. This instantaneous production of light is achieved by the use of electronic ballasts. Ballast is a device which controls the starting voltage and the operating currents of lighting devices built on the principle of electrical gas discharge. It refers to that part of the circuit which limits the flow of current through the lighting device and may vary from being a single resistor to a bigger, complex device. In some fluorescent lighting systems like dimmers, it is also responsible for the controlled flow of electrical energy to heat the lamp electrodes.
Insight – How Electronic Ballast works
Electronic ballasts are gradually replacing conventional magnetic ballasts (commonly known as choke) from the fluorescent tubes. They have higher efficiency as compared to magnetic ballasts and provide a flicker free start up to the tube. Also it does not produce the ‘hum’ sound which is very annoying with the magnetic ballastElectronic ballast uses semiconductor components and operates at 20 KHz-80KHz unlike the magnetic ballast which operates at 50 -60 Hz. At high frequency the lamp requires less input power, thereby increasing the efficiency. When power supply enters in to the ballast circuit, it first goes through an EMI filtration to block the ballast generated noise. Capacitors are used for the same.
Insight – How Adaptor works
In today’s world most of the electronic appliances needs DC voltages from 3-12volts for operation. An adaptor is a device which is used to convert high AC voltages to low DC voltage. Adaptors come in various shapes, sizes & configuration depending on the use. In some cases adaptors are used to provide power to electronic appliances like video games, modems etc and in some cases they are used to charge the primary battery of the electronic device and also act as alternate power source like mobile chargers, laptop chargers, cell chargers etc. A typical adaptor is shown in the figure below.
Simple AC to DC converter using bridge rectifier
An AC power source is required for powering major appliances but almost all electronic circuits require a steady DC supply. A simple rectifier circuit described in [[wysiwyg_imageupload::]]this project converts the input from AC source to DC voltage. Firstly, the AC input from mains is stepped down to a lower value of voltage. This AC supply is then passed through a rectifier circuit to remove the negative cycle of AC waveform. The resulting signal is then filtered to get the DC output. The major part of the circuit is connected to the secondary coil of the transformer which is comprised by diodes and capacitor. While the diodes act as actifiers, capacitor filters out the DC component from the circuit.