In a previous tutorial, we discussed the MIT App Inventor, a popular online platform for building mobile applications using visual programming. The platform is helpful for quickly prototyping Internet-of-Things (IoT) applications and simple embedded systems that interact with mobile devices. We already reviewed the platform’s architecture and user interface. Its visual programming platform is ideal for…
How to connect Arduino to PC over Ethernet Technology and MQTT Protocol : IOT Part 24
In the previous tutorial, the basics of Ethernet technology were discussed. In this tutorial, the Ethernet technology will be used to connect an Arduino board over internet with a PC. The Arduino based IOT device and the PC will be setup to communicate using MQTT protocol via HiveMQ Broker. An IOT device based on Arduino will be designed in this project. The Arduino will be interfaced with an Arduino Ethernet Shield to connect with a router via Ethernet cable (Cat 5e).
Configuring SIM800 Modem using a PC as server over TCP-IP Protocol: IOT Part 26
SIM800 is a popular GSM GPRS modem. It supports General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) for connecting to the Internet. This module has built-in TCP/IP stack that can be accessed serially with AT commands.The modem needs to be configured by connecting it to a PC. In such setup, the SIM800 modem with SIM card acts as TCP client and the PC acts as TCP server.
GPRS Technology-General Packet Radio Service : IOT Part 25
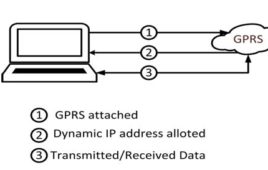
In the previous tutorial, the Ethernet technology was used to connect an Arduino based IOT device with the internet network. The IOT devices can also be connected to internet network using mobile technologies like GSM, CDMA and GPRS. There are two major technologies for data transfers over cellular networks – GSM and GPRS. These two technologies differ from each other on the basis of data rates and the charges they take for their operation.
ESP8266 based IOT Temperature Monitor using Adafruit Broker : IOT Part 21
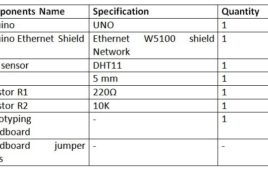
In the previous tutorial, ESP8266 module was used to design a Home Area Network to control an LED light from a remote PC. The PC client was used to send control signals to switch on and off the LED light in the Home Area Network. In this tutorial, the ESP module will be interfaced with DHT-11 temperature sensor and temperature data will be sent to the PC client for real-time temperature monitoring. In this project, instead of LED, the DHT-11 sensor will be interfaced with the ESP8266 on ESP Client side.
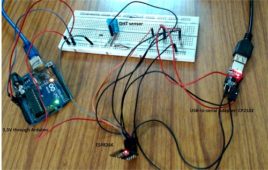
Security Enabled M2M Communication using CloudMQTT Broker : IOT Part 19
Security is a prime concern in any IoT application development. The data from the IoT devices is passed to the server/cloud where it may be stored temporarily or for long time to generate analytics. The transportation medium through which the data is passed from the IoT device to the cloud must be secured with implementation of various IoT security measures, so that the data could not be hacked by any Man-in-the-Middle attack.
How to Communicate between PC and Mobile using MQTT Protocol Via HiveMQ Broker : IOT Part 18
In the previous tutorial, it was learnt that how a smart phone and a PC can be set up as MQTT clients and their connection with an MQTT broker can be established. The smart phone was configured as an MQTT client using an android MQTT app – IOT MQTT Dashboard while the PC was configured as MQTT client using a chrome add-on – MQTTLens.Now, in this tutorial, these MQTT clients – Mobile and PC will be made to communicate with each other using MQTT protocol. The communication between the MQTT clients is only possible via MQTT broker.
What temperature sensors are used for electronics and IoT devices?
Temperature sensors are commonly used in embedded applications to monitor ambient temperature and prevent overheating. As a thermal management of the device, these sensors can issue a warning or trigger a cooling mechanism. However, the use of these sensors varies, depending on the application. For example, temperature sensors are used in: Industrial equipment for process…
What is Matter? An all-new smart home standard
Smart home automation is continuously evolving. It’s an emerging segment that has attracted the attention of big tech conglomerates like Apple, Google, and Amazon. However, interoperability has been a significant challenge in smart home installation since its inception. The focus so far has been on integrating a myriad of devices, platforms, and services under a…
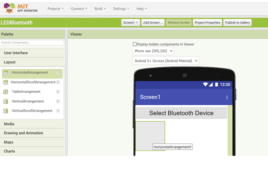
How to get started with MIT App Inventor
Mobile apps play a crucial role in the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem, serving as interfaces through which users can interact with and control IoT devices. Several IoT devices used in consumer electronics, home automation, logistics and inventory, and others are controlled or managed through mobile applications. For example, users can rely on an app…
How to encode & decode JSON data in Arduino for IoT
JSON and XML are the most common data serialization formats. The Internet is a hub of billions of different devices, applications, and services. These devices and applications are built in different programming languages and around diverse platforms. For all these entirely different devices and applications to effectively communicate with each other, data is serialized and…
Raspberry Pi Server based Hotel/Restaurant Order Management System on IoT – IOT Part 46
Nowadays, most of the hotels and restaurants take online orders of food. Many hotels and restaurants either facilitate pre-ordering or even render delivery services in the local areas. In this project, an Hotel Order Management System is designed where a customer can pre-order food items using a mobile app and a Raspberry Pi based Server manages to cater menu items and book orders.
How to manage data on ESP32 for IoT projects
ESP32 is a powerful 32-bit controller that clocks at speeds 160~240 MHz. Designed for IoT, the controller has on-chip Wi-Fi (40 MHz), Bluetooth 4.0, Bluetooth Low Energy, CAN, and an Ethernet interface. With 34 GPIO, 18 analog pins, 16 software PWM channels, 4 SPI ports, 2 I2C ports, 2 I2S ports, and 2 UART ports,…
Controlling an LED Light with PC using ESP8266 based HAN and HiveMQ Broker : IOT Part 20
Internet of Things is meant to empower objects of day to day use with embedded electronics and IT infrastructure. It aims to connect these objects in real time with the internet network and allow them to communicate with other co-located or remote objects. For communicating with each other, the IOT devices need to follow protocols. An application developer need to take care primarily of the implementation of application layer protocols while usually the implementation of network and transportation layer protocols remain at the hand of network administrators or network programmers.
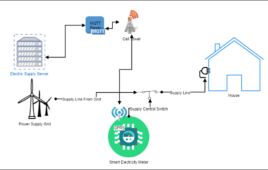
IoT-based, pre-paid electricity system
In this article, we will be making an IoT-based pre-paid electricity system and learn exactly how that works. We will create a meter that will monitor the electricity usage and report to a monitoring server (which we will also create) for bills. In an ordinary electricity system, bills come after the usage, and then we…
How to make HTTP requests using Arduino for the IoT
One essential step in developing Internet of Things (IoT) applications is setting up communication between the IoT devices and a web server or services. IoT devices communicate with a web server, service, or an API through HTTP requests. An HTTP request is a message sent by a client to a server in the context of…
Controlling IoT Devices through Emails over IMAP Protocol – IOT Part 48
In the previous tutorial, it was mentioned that IMAP protocol is a standard email protocol which is used to store email messages and retrieve them. It was also mentioned that IMAP protocol can be used in IoT applications where commands can be passed to IoT devices by emails. This can be really helpful in certain situations like when security might be the main concern. Also, emails can be sent on any network without any special application or permissions. The IoT devices can receive emails as email clients where they can read emails and process information contained in them.
Secure client server communication over TLS security protocol using Mosquitto Broker: IOT Part 42
Transport Layer Security (TLS) is a security protocol which uses symmetric cryptography to secure data. In this tutorial, Client-Server communication will be setup using TLS Protocol so that data can be securely exchanged between them. The Mosquitto broker is used to provide TLS security. The Mosquitto broker uses 8883 port as an encrypted transmission port to securely exchange the data between clients.
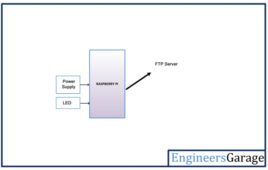
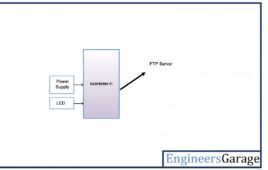
Application of FTP Protocol in Internet of Things – IOT Part 43
File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a standard protocol for transferring files between a client and server over an internet network. The FTP protocol was written by Abhay Bhushan (IIT Kanpur) in 1971. In 1980, a TCP/IP version of the protocol as RFC 765 was introduced which became the de facto standard worldwide. in 1998, the protocol stack was updated for IPv6 support. Within this protocol, the security features were enabled by a TLS/SSL layers called FTP Secure (FTPS). A new secured version of FTP is also widely used called SSH File transfer protocol (SFTP). The SFTP is quite different protocol than the traditional FTPS.
Automatic Software Update by IoT Device over FTP Protocol – IOT Part 44
In the previous tutorial, FTP protocol and file transfer over it between a Client and Server was discussed. The FTP protocol can really useful in many IoT applications. Many IOT devices are installed in places like nuclear plant, electrical grids and other industrial setups where these types of devices can get some bugs and need application software updates to fix them. On standard IoT protocols like MQTT, CoAP, etc, it is hard to update and reinstall application software because most of the IoT protocols are designed for IoT communication between devices and network but not for tasks like application updates.