The circuit presented here operates a relay for Fixed Timer Interval. So the device or machine connected with relay operates for same time. The device once switched ON, automatically switches OFF after Fixed (set) Time Interval when relay switches OFF. The Time Interval can be varied and it is displayed on 7 Segment Display. This kind of circuits can be used in many applications where it is required to operate any device or machine for Fixed Time Interval. Like
· The Alarm Signal (or Bell) once triggered, remains ON for Fixed Time Interval and then shuts off automatically
· In Manufacturing Industries the Motors have to be rotated for Fixed Time Interval once start button is pressed. It stops automatically when time period is over
Time operated relay circuit is build using IC555. To display the time period in seconds 2-digit decade counter is build using CD4026 chip. Another IC555 is used to provide 1 Hz pulse to update time period after every 1 sec.
The circuit presented here operates a relay for Fixed Timer Interval. So the device or machine connected with relay operates for same time. The device once switched ON, automatically switches OFF after Fixed (set) Time Interval when relay switches OFF. The Time Interval can be varied and it is displayed on 7 Segment Display. This kind of circuits can be used in many applications where it is required to operate any device or machine for Fixed Time Interval. Like
· The Alarm Signal (or Bell) once triggered, remains ON for Fixed Time Interval and then shuts off automatically
· In Manufacturing Industries the Motors have to be rotated for Fixed Time Interval once start button is pressed. It stops automatically when time period is over
Time operated relay circuit is build using IC555. To display the time period in seconds 2-digit decade counter is build using CD4026 chip. Another IC555 is used to provide 1 Hz pulse to update time period after every 1 sec.
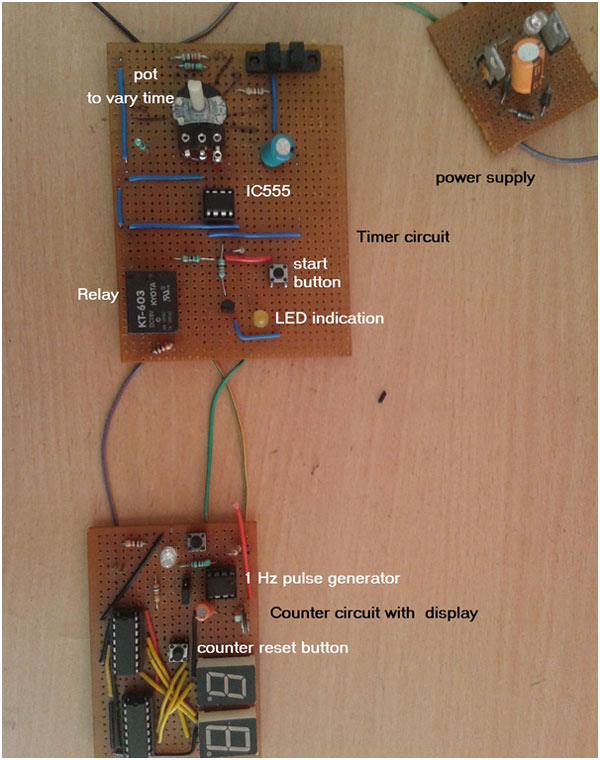
Fig. 1: Prototypes of 555 IC based Timer and Digital Counter
Circuit Description
The circuit is divided in 2 sections
1. Timer Circuit
2. Counter Circuit
Timer Circuit
This is the circuit (Please refer Circuit Diagram Tab) that switches ON relay for set time period. It is build using IC555. IC555 is configured in monostable mode. Its time period is determined by RC components R2 and C3. R2 is 100 K variable resistance so we can vary the time period. Minimum and maximum time period can be calculated as
Tmax = 1.1 × R2max × C3
= 1.1 × 101 × 103 × 100 × 10-6
= 11 sec
And Tmin = 1.1 × R2min × C3
= 1.1 × 1000 × 100 × 10-6
= 0.11 sec
Note
For experiment the RC values are kept smaller to get time interval in seconds. But by choosing larger values of R and C the time interval can be set in 10s of second or in minutes also.
The output of IC555 drives three components
· First, it drives LED2 through current limiting resistor. LED2 is used to indicate relay is ON
· Second it drives 1 C/O (change over) relay through NPN transistor. Any load or machine or device is connected with C (common) and NO (normally open) terminals of relay
· Third it drives reset pin of another IC555
Another IC555 is connected in astable mode. Its output frequency is determined by 100 K pot R5 and 10 uF capacitor C1. Its frequency is set to 1 Hz by varying pot R5. So LED1 blinks at every 1 sec. Output of this IC555 is given as clock pulse to counter circuit.
Counter Circuit & Circuit Operation
Counter Circuit
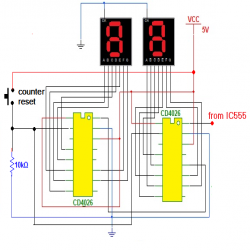
2-digit counter circuit is built using two decade counter cum display driver chips CD4026. The 1 Hz pulse output from IC555 is directly given as clock pulse input (pin 1) to 1st CD4026. (Please refer Circuit Diagram 2nd Tab)
It increment its count by 1 on every pulse input. Also it converts the count into equivalent 7-segment display code (common cathode) so that count can be displayed. It counts from 0 to 9 and again resets to 0. When it goes from 9 to 0, it generates output pulse (carry out) that can be given to next decade counter chip. So as shown in figure the carry out (pin 5) of 1st decade counter is given as clock input (pin 1) to 2nd decade counter chip. The outputs of both decade counter chips (CD4026) are, a, b, c, d, e, f, and g that can be directly given to respective inputs to common cathode type 7 segment displays. The outputs of chip CD4026 are connected to a-b-c-d-e-f-g inputs of both 7 segment displays as shown. As the count increments it is displayed on these displays from 00 to 99 and again 00. Because they are common cathode type displays, their common terminals are grounded. To reset both chips to 0 it is required to give high pulse on reset pin (no 15). So one push button is connected to reset pins of both chips as shown, to reset counter to 00 normally both reset pins are connected to ground through 10 K resistor.
Circuit Operation
· When supply is given, relay and LED1 (yellow) are off. Astable mustivibrator IC is also off so it does not generate 1 Hz pulses. The counter displays 00 on seven segment. If it does not then by pressing counter reset button the it can be reset to 00
· Set the desire time between 0.1 to 11 sec by setting pot at proper value
· Trigger is applied to timer IC555 by pressing start push button
· IC555 output goes high. So relay is switched ON that is indicated by yellow LED
· At the same time the reset pin of second IC555 also becomes high
· So it start generating 1 Hz pulses that is given to counter
· So counter starts incrementing after every second as 0, 1, 2, ……
· After the set time period (say 6 sec) timer IC555, its output goes low
· So relay is OFF, LED1 is also off and reset pin of 2nd IC555 goes low
· So it stops generating pulses that makes counter stops counting
· Last count is displayed on 7 segment
· So we can observe for how much time the relay was ON
· Again set any different time interval by changing pot value and press start button
· The same process repeats
You may also like:
Circuit Diagrams
Project Components
Project Video
Filed Under: Circuit Design, Electronic Projects
Filed Under: Circuit Design, Electronic Projects







Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on EDAboard.com and Electro-Tech-Online.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.